If the HDD makes strange sounds or there are problems with writing and reading information, you should use one of the programs to check hard drive for errors. Depending on the task (checking the disk surface for damage, searching bad sectors, error correction, etc.) various software may be useful.
You can quickly check the disk for errors using standard system tools, but to restore the hard drive you will need special third-party programs. Having learned how to check the health of a hard drive using various utilities, a user of any level will be able to cope with any problems that may arise.
CheckDisk System Service is the simplest hard drive diagnostic program that can't find complex errors or fix bad sectors, but is useful for fixing basic problems. It is available on all versions of Windows OS and can be used to check drives of any type. All users need to know how to check a hard drive for errors with this tool.
Utility version with graphical interface most convenient for novice users. You can launch it through the disk management menu, which can be accessed in two ways:
- in Windows XP/Vista/7 - select “Manage” in the context menu of “My Computer”, then go to the desired menu;
- in Windows 8/10 - press the Win+X combination and select the appropriate item.
In the window that opens, select the device that needs analysis, right-click on it and select “Properties” from the drop-down menu. By going to the “Service” tab, you need to run the hard drive diagnostic program.
The system will check and automatically correct errors if the disk is not currently busy with read or write processes. Otherwise, the program will offer to test after rebooting the PC. If necessary, in the scan results window you can see detailed information about the HDD status.
The GUI version does not always help, since checking the status of the hard drive is sometimes required from safe mode or without starting the operating system at all. In such cases, the console comes to the rescue; you can launch it before the system starts using boot disk.
Once you open the recovery console, you need to run the chkdsk /f command, which will check all connected drives. In some cases, this will help fix the error. However, in most situations, if a HDD failure has made it impossible to start the system, a more in-depth check of the hard drive’s condition will be required.
To use the console command from inside the system you need to:
- launch the command line (via Win+X or by entering cmd in the “Run” window);
- enter the chkdsk command indicating the letter of the partition being checked and additional flags;
- Confirm the operation by pressing Y.
Checking the HDD via the command line will be a little faster than when using the GUI version of the program; the results will be shown here in the console.
The Linux system also has standard tools - hdparm and smartctl, launched from the console.
Simple programs for quickly checking HDD
If standard utilities are not suitable, hard drive diagnostics can be carried out using simple third party programs. They allow you to get more information about the health status of the HDD, but in case of serious problems they will not be suitable, since they cannot be used to fix the damage.
HDDScan is a free program that performs analysis in two modes:
- according to S.M.A.R.T. indicators;
- linear processing.
The tool evaluates the read and write speed of various sectors, marking the “slow” cells. During the analysis, the program ensures that the tested hard drives do not overheat; at the end of processing, the user is presented with a full report.
HDDScan good versatility. The utility allows you to check disks for errors, regardless of the type of device: you can use it to check how external hard disk, and analyze a RAID array, SSD drive or memory card.
Crystal Disk Mark has only one function - it evaluates the read and write speed. Despite this, it is often used, since it is still possible to check the hard drive for serviceability using just two indicators.
The test uses different algorithms, one of which is sequential recording mode. The program gradually fills all the space on the drive with blocks of a size specified by the user, after which it cleans the HDD. The same technique is used by hard drive manufacturers to check product quality. Its disadvantage is that it accelerates the wear of SSD drives.
CrystalDiskInfo And DiskCheckup They are similar in their set of functions, differing only in the interface. They check the status of the hard drive using S.M.A.R.T. algorithms and compile a history of checks, which allows you to track the dynamics of changes. CrystalDiskInfo has more options for visualizing history. For example, you can create a graph, not just get a written report.
Another feature of these programs is a convenient notification system. In-depth hard drive tests usually take a long time. If the user needs to step away from the computer, he can enable notifications of critical HDD errors via E-Mail.
Programs from hard drive manufacturers
Some HDD manufacturers have developed their own utilities to analyze the status of the hard drive. They are intended for use with devices of the same name; diagnosing a hard drive from another company is possible with their help, but this must be done carefully. Unlike simpler programs, these utilities have versions in different languages, including Russian. Which program is better to analyze the HDD status?
The proprietary program from Seagate exists in two versions: a standard version for running under Windows and a DOS version in ISO image format, from which you can make a bootable USB flash drive. It is recommended to use the second option, since the check in this case will be more accurate and efficient.
SeaTools uses part of the S.M.A.R.T indicators. to test the hard drive without giving away details about each item. Three tests can be performed:
- short self-test of HDD;
- short rapid test;
- a long-term check in which all sectors are read sequentially.
As the scan progresses, the program automatically corrects any errors found.
Owners of hard drives from WD should know how to check the performance of hard drives using proprietary software from this manufacturer. The range of its capabilities is similar to that of the program from Seagate, but is somewhat expanded and allows for more in-depth work with the affected device.
There are two additional functions:
- deep disk formatting - the program writes zeros to all sectors, permanently destroying information;
- blocking access to bad sectors - the program marks bad blocks, preventing the writing of new information to them.
Unlike SeaTools, this HDD diagnostic program can be freely used with devices from any manufacturer to check the hard drive for errors - no problems were identified with this.
Deep testing software
If you need not only checking your hard drive for errors, but also correcting bad sectors, you cannot do without a complex software, which carries out the most in-depth analysis of the HDD state.
Victoria HDD
According to many users, Victoria HDD is the best software for detecting hard drive problems. The program gained this reputation due to its wide range of functions.
Victoria exists in two versions:
- with a graphical shell for use from inside Windows;
- with a DOS shell to create a boot disk.
It's better to use the second version. Diagnostics of the HDD outside the system allows you to achieve better results, so it is always recommended to follow the principle “if possible, test the disk from the boot disk.” As a last resort, you can use a LiveCD of another OS, for example, Linux distribution like Ubuntu.
Victoria HDD has a variety of functions:
- quick and complete disk scan;
- reassignment of bad sectors and their restoration;
- checking the status of contacts in the IDE or SATA cable;
- equipment performance analysis;
- viewing S.M.A.R.T. indicators.
When checking, you need to pay attention to the access time to sectors. It should not exceed 200-600 ms. You can also view the temperature of the disk during operation, but this is not so important.
HDD Regenerator
HDD Regenerator is a program for professional hard drive recovery. It not only marks bad sectors as unused, but also tries to revive them. For this, not the standard deep formatting method is used, but a proprietary algorithm based on transmitting signals of different levels to the sector. Despite its professional level, inexperienced users can also use this software, since testing a hard drive with its help is not difficult thanks to its convenient Russian-language interface.
Program features:
- ensuring data safety - it works only in read mode;
- support for different file systems;
- the ability to scan the disk surface;
- real-time monitoring.
The program is not suitable for everyone, since you can check your hard drive for functionality for free, but you will have to pay $90 for the sector recovery function.
If you don’t want to pay, you can use TestDisk, a free program that can restore the partition table, boot sectors and MFT. It also detects bad sectors, can recover deleted information and fix errors file system. The only drawback is the lack of a graphical interface; you have to work from the console.
If, after checking the HDD and correcting all problems, the computer does not stop working incorrectly, it is worth checking the registry. Perhaps the failures are caused not by hardware failure, but by internal system errors.
Hello dear blog readers. — hard restoration disk, this is the topic of our article today. The last issue was dedicated.
To treat your computer - Windows and hard sections disk there is a special program CHKDSK, which anyone can use.
You will learn how to enter it and what steps you need to take to restore Windows and partitions on your hard drive in this article.
Recovering the disk
Your computer has stopped functioning normally, Windows boots every once in a while or doesn’t boot at all, you hear strange, repeating sounds and noises from the system unit. What could be the matter, you ask me?
Most likely, one of the fans located inside the system unit is noisy. It is also possible that the hard drive is making such noise - it does not have enough power, it has errors or it will soon fail, this happens. You need to think about buying a new one and saving the information on the old hard drive as long as possible.
As I said above, the Windows operating system has a built-in chkdsk utility, with which you can check your hard drive for errors and restore operation operating system if it doesn't load.
This method does not always work, but in most cases in my practice, using the chkdsk program, it was possible to restore the previous functionality of the Windows operating system. They can also help you.
There are three ways to run chkdsk on your computer:
- Running chkdsk from Windows
Running chkdsk on Windows
You can use this method if it works fine for you Windows system and you want to check your hard drive for errors.
Go to My Computer.

Right-click on the desired logical drive (C, D, E, etc.).
In the pop-up menu, go to the very bottom and select “Properties”.

In the window that appears between the top tabs “General” and “Equipment” - go to “Service”.

Select “Check disk for errors” and go to “Run check”.

Disk scan options - check the two proposed options: “Automatically correct system errors” and “Scan and repair bad sectors”, click the Start button.

If the disk is currently in use, you will be prompted to disconnect this volume.

After you disconnect this volume, a disk scan will begin, which may take some time and will depend on the amount of information on this logical disk.

If this is a system drive on which the operating system is installed, then you will be prompted to run this check after rebooting the computer. You need to click Schedule scan and restart your computer.

After restarting the computer, when using Windows Vista and Windows 7 will display a black window with white letters.

If you are using Windows XP, the window will be blue. We don’t press anything and wait 10 seconds, after which 3 to 5 tests will run, on average it takes from half an hour to several hours.

At the end of the check, the computer will reboot itself and will operate in normal mode.
It is important to know! If you do not wait for this check to complete, restart your computer yourself. The next time you turn it on, you will receive a message about the disk check until you complete it.
Running the chkdsk utility from the command line
If you are a lover of Dos and command line, or just want to see how the chkdsk utility works on the command line, you can use this method.
First of all, you need to press the key combination Win + R (English) K (Russian) on your keyboard, thereby taking us to Run the program or Run. Here's a screenshot for clarity, if you don't understand what we're talking about:

A small Run window appears, where you need to type the command, write the desired [volume:] (logical hard drive), for example, and specify the command for further operations or. Here's an example.
A little more detail:
- - team name.
- [Volume:] is a logical hard drive.
- — is set to correct errors on a logical disk.
- — is set to detect bad (damaged) sectors and restore the part that can be read.

You need to wait a little and the chkdsk program running in DOS will appear in front of you. The volume you selected must pass five tests. This procedure can take a long time, especially the last fifth test.

After all the checks, the next time you restart the computer, a window with a check disk may appear, which were described in the last paragraphs of the first method of launching the shkdsk program. So be prepared for this.
Running chkdsk using the Windows boot disk
Let's say that when you boot your computer, Windows constantly reboots at the initial boot stage or a black screen just appears. There is a second way to use or how to run CHKDSK, but for this you must have a Windows boot disk handy.
Thank you for reading me on
One of the important factors in system performance is the health of such basic components as hard drives. It is especially important that there are no problems with the drive on which the system is installed. Otherwise, problems such as the inability to access individual folders or files, regular emergency logout from the system, “ blue screen death" (BSOD), up to the inability to start the computer at all. Let's find out how you can check your hard drive for errors on Windows 7.
If you have a situation where you can’t even log into the system, then in order to check whether problems on the hard drive are to blame, you should connect the drive to another computer or boot the system using a Live CD. This is also recommended if you are going to check the drive where the system is installed.
Checking methods are divided into options using exclusively internal Windows tools (utility Check Disk) and options using third-party software. At the same time, the errors themselves can also be divided into two groups:
- logical errors (file system corruption);
- physical (hardware) problems.
In the first case, many programs for studying the hard drive can not only find errors, but also correct them. In the second case, using the application it will not be possible to completely eliminate the problem, but only mark the bad sector as unreadable so that no more writing is done there. Complete hardware problems with a hard drive can only be resolved by repairing or replacing it.
Method 1: CrystalDiskInfo
Let's start by analyzing options using third-party programs. One of the most popular ways to check a HDD for errors is to use the well-known utility CrystalDiskInfo, the main purpose of which is precisely to solve the problem under study.


If several physical HDDs are connected to the computer at once, then to switch between them in order to obtain information, click on the menu "Disk", and then select the desired media from the list.

Advantages this method using CrystalDiskInfo lies in the simplicity and speed of research. But at the same time, with its help, unfortunately, it will not be possible to eliminate problems if they are identified. In addition, it must be recognized that searching for problems using this method is quite superficial.
Method 2: HDDlife Pro
The next program that will help assess the condition of the drive used under Windows 7 is HDDlife Pro.


To update the data, you need to click in the main window of HDDlife Pro "File" and then select "Check disks now!".

The main disadvantage of this method is that the full functionality of HDDlife Pro is paid.
Method 3: HDDScan
The next program with which you can check your HDD is the free HDDScan utility.
- Activate HDDScan. In field "Select Drive" The name of the HDD that needs to be manipulated is displayed. If several HDDs are connected to the computer, then by clicking on this field, you can choose between them.
- To start scanning, click the button "New Task", which is located to the right of the drive selection area. Select from the drop-down list "Surface Test".
- After this, a window for selecting the test type opens. There are four options to choose from. By moving the radio button between them:
- Read(default);
- Verify;
- Butterfly Read;
- Erase.
The latter option also involves completely clearing all sectors of the scanned disk of information. Therefore, it should be used only if you consciously want to clean the drive, otherwise the necessary information will simply be lost. So this function should be used very carefully. The first three items on the list represent testing using various reading methods. But there is no fundamental difference between them. Therefore, you can use any option, although it is still preferable to use the one that is installed by default, that is, "Read".
In the fields "Start LBA" And "End LBA" You can specify the start and end sectors of scanning. In field "Block Size" indicates the cluster size. In most cases, these settings do not need to be changed. This way you will scan the entire drive, rather than just one part of it.
Once the settings are set, press "Add Test".
- In the bottom field of the program "Test Manager", according to the previously entered parameters, a testing task will be generated. To run the test, simply double-click on its name.
- The testing procedure is launched, the progress of which can be monitored using a graph.
- After completing the test in the tab "Map" you can view its results. A working HDD should have no broken clusters, marked in blue, and clusters with a response exceeding 50 ms, marked in red. In addition, it is desirable that the number of clusters marked in yellow (response range from 150 to 500 ms) be relatively small. Thus, the more clusters with minimal response time, the better the HDD state is considered.






Method 4: Check with the Check Disk utility through the drive properties
But you can check the HDD for errors, as well as correct some of them, using the built-in Windows 7 utility, which is called Check Disk. It can be launched in various ways. One of these methods involves launching through the drive properties window.
- Click "Start". Next, select from the menu "Computer".
- A window will open with a list of connected drives. Right click ( RMB) by the name of the drive you want to check for errors. From context menu select "Properties".
- In the properties window that appears, move to the tab "Service".
- In the block "Check Disk" click "Run check".
- The HDD check window opens. In addition to the actual research by checking and unchecking the corresponding items, you can turn on or off two additional functions:
- Scan and repair bad sectors(disabled by default);
- Automatically fix system errors(enabled by default).
To activate scanning, after setting the above parameters, click "Launch".
- If you selected the settings option with recovery bad sectors, then an information message will appear in a new window indicating that Windows cannot start checking the HDD that is in use. To start it, you will be prompted to dismount the volume. To do this, click on the button "Disable".
- After this, scanning should begin. If you want to check the system drive on which Windows is installed with a fix, then in this case you will not be able to disable it. A window will appear where you should click "Disk check schedule". In this case, the scan will be scheduled the next time you restart your computer.
- If you unchecked the item "Check and repair bad sectors", then scanning will start immediately after completing step 5 of these instructions. The procedure for examining the selected drive is performed.
- After the procedure is completed, a message will appear indicating that the HDD has been successfully verified. If problems are detected and corrected, this will also be reported in this window. To exit, click "Close".









Method 5: "Command Line"
The Check Disk utility can also be launched from "Command line".


If the user wants not only to conduct research, but also to automatically correct errors found during the process, then in this case the following command should be entered:
Press to activate Enter.

If you need to check the drive for not only logical, but also physical errors (damage), and also try to fix damaged sectors, then in this case the following command is used:

When checking not the entire hard drive, but a specific logical drive, you need to enter its name. For example, in order to scan only a partition D, you should enter such an expression in "Command line":

Accordingly, if you need to scan another disk, you need to enter its name.
Attributes "/f" And "/r" are basic when running the command chkdsk through "Command line", but there is also whole line additional attributes:
- /x– disables the specified drive for a more detailed check (most often used simultaneously with the attribute "/f");
- /v– indicates the cause of the problem (can only be used in the NTFS file system);
- /c– skipping scanning in structural folders (this reduces the quality of the scan, but increases its speed);
- /i– quick check without details;
- /b– re-evaluation of damaged elements after an attempt to fix them (used exclusively in conjunction with the attribute "/r");
- /spotfix– spot error correction (works only with NTFS);
- /freeorphanedchains– instead of restoring contents, it clears clusters (works only with FAT/FAT32/exFAT file systems);
- /l:size– indicates the size of the log file in case of an emergency exit (without specifying the size, the current value remains);
- /offlinescanandfix– offline scanning with disconnection of the specified HDD;
- /scan– proactive scanning;
- /perf– increasing the scanning priority over other processes running in the system (applied only in conjunction with the attribute "/scan");
- /? – calling the list and attribute functions displayed through the window "Command line".

Most of the above attributes can be used not only individually, but also together. For example, entering the following command:
chkdsk C: /f /r /i
will allow you to quickly check the partition C without detail with correction of logical errors and bad sectors.

If you are trying to perform a scan and fix the disk on which the Windows system is located, then you will not be able to perform this procedure right away. This is due to the fact that this process requires an exclusive right, and the functioning of the OS will prevent this condition from being fulfilled. In this case, in "Command line" A message appears stating that the operation cannot be performed immediately, but it is suggested that this be done the next time the operating system is restarted. If you agree with this proposal, then you should press on your keyboard "Y", which symbolizes “Yes”. If you change your mind about carrying out the procedure, then click "N", which symbolizes “No”. After entering the command, press Enter.

Method 6: Windows PowerShell
Another option for starting the media scanning procedure for errors is to use the built-in Windows PowerShell tool.
- To access this tool, click "Start". Then "Control Panel".
- Sign in "System and safety".
- Next select "Administration".
- A list of various system tools appears. Find "Windows PowerShell Modules" and click on it RMB. From the list, select "Run as administrator".
- A PowerShell window appears. To start a partition scan D enter the expression:
Repair-Volume-DriveLetter D
At the end of this expression "D"— this is the name of the partition being checked; if you want to check another logical drive, then enter its name. Unlike "Command line", the bearer's name is entered without a colon.
After entering the command, press Enter.

If the results show the value "NoErrorsFound", this means that no errors were found.
If you need to perform an offline media check D with the disk disconnected, then in this case the command will be like this:
Repair-Volume -DriveLetter D –OfflineScanAndFix
Again, if necessary, you can replace the partition letter in this expression to any other. After entering, press Enter.





As you can see, you can check your hard drive for errors in Windows 7 either using a number of third-party programs or using the built-in utility Check Disk, running it in various ways. Error checking involves not only scanning media, but also the ability to subsequently correct problems. However, it should be noted that it is better not to use such utilities too often. They can be used when one of the problems that were described at the beginning of the article appears. For preventative purposes, it is recommended to run programs to check the drive no more than once every six months.
Crashes in Windows work, an emergency shutdown of the computer's power, experiments with software for managing disk space, the consequences of viruses - these and other problems can lead to the automatic launch of the standard Windows Chkdsk utility, designed to correct errors in the file system of hard drives. Incorrectly completed operation of the operating system with files leads to file system errors, and sometimes even damage to the file system. In emergency cases, the Chkdsk utility turns on itself before Windows starts, scans disk partitions and corrects errors. However, the fact that there are problems with the file system may not make itself felt during normal use of the computer and only become apparent when trying to manage disk space. So, for example, trying to reduce a disk partition with standard using Windows, we may receive the following notification: “It is possible that the volume selected for compression is damaged. Use Chkdsk to troubleshoot the problem, and then try shrinking the volume again."
In this case, disk check will not start automatically. How to run Chkdsk manually in Windows 7, 8.1 and 10? How can I use Chkdsk to fix disk errors if this problem is the reason the operating system is unable to boot?
Inside Windows utility Chkdsk can be launched in several ways.
1. Run Chkdsk using Windows GUI
To run Chkdsk, in the system explorer on drive C, right-click and open “Properties”.

In the disk partition properties window that opens, go to the “Services” tab, and in it click the “Check” button (or “Run check” for Windows 7).

In versions of Windows 8.1 and 10, if everything is in order with the disk file system, in the window that appears next, we will see a notification that checking is not required. But if you wish, you can start checking the disk with the Chkdsk utility by clicking “Check disk”.

If the system suspects file system errors, this window will contain a button to start scanning and repairing the disk.

For Chkdsk to work relative to drive C, you must restart the computer. You can do this immediately or delay running the scan until the next reboot.

After restarting the computer, we will be able to observe the operation of Chkdsk.

In Windows 7, launching Chkdsk is slightly different: to the preinstalled option of automatic error correction, you can add another possible option - checking and repairing bad sectors of the hard drive. When activating this option, it is worth considering that in this case Chkdsk may take longer to run.

As with Windows 8.1 and 10, in version 7 the system drive C cannot be scanned within a running operating system. To start the scan, the computer must be restarted. Click “Schedule disk check”.


When checking a non-system partition of a disk, if it is used by some programs, the situation is simpler than with the system partition. In the window with a notification that the disk is currently in use, you just need to click the “Disconnect” button to, accordingly, disable this partition for the duration of the scan.
2. Run Chkdsk using the command line
To run Chkdsk using the command line, first, accordingly, launch the latter.
In the command line enter a command like this:
In this command, instead of drive C, we each time substitute the letter of the desired partition on which the scan is required. If Chkdsk needs to check the system partition C, as with the GUI, you will need to restart the computer. When a message appears in the command line about the impossibility of locking the specified drive, you need to enter “Y”, then restart the computer.

In addition to the /f parameter, which is responsible for correcting disk errors, Chkdsk can be run with the /r parameter, designed to search for bad sectors and restore data. As a result of Chkdsk running with this parameter, hard disk clusters with unreadable sectors will be listed as damaged (bad blocks) and their functions will be transferred to a new cluster. Therefore, it is recommended to run Chkdsk with the /r parameter only when the usual error correction - running the utility with the /f parameter - does not bring the necessary results. Using the same drive C as an example, the command would look like this:
3. Running Chkdsk on a non-booting Windows
If Windows freezes at a certain point in the boot process, one of the possible causes of this problem is file system errors. In this case, you need to run Chkdsk by booting from the rescue media. As such, you can use regular installation media with versions of Windows 7, 8.1 or 10. With its help, we will launch the Chkdsk utility inside the command line. At the first stage of starting the system installation process, press the command line launch keys – Shift+F10.

In the command line that opens, before running the Chkdsk command, you need to clarify which letters define the disk partitions. This is easy to do with a notepad. I launch it with the command:
Click the notepad menu “File”, then “Open”.

In the explorer that opens, remember the new drive designations. As a rule, in Windows 8.1 and 10, the C drive partition (as it exists inside the running operating system) is listed as D, since the letter C is assigned to the first technical partition of the system. And all other sections are shifted by one letter of the alphabet.

Having decided on the letters of the disk partitions, close Notepad, then, returning to the command line, enter a command like this:


As with Chkdsk inside Windows, you must first try to fix disk errors by running the utility with the /f parameter. And only if the problem is not solved, only then run the command with the /r parameter, as indicated in the previous paragraph of the article.
If Windows is unable to boot, you can pre-burn an emergency Live disk with a selection of various tools to restore the operating system. Among these, for example, is AdminPE based on WinPE. Its image for recording on a disk or flash drive can be downloaded from the official website of the project Adminpe.Ru. Using AdminPE, you can launch a command prompt and enter the Chkdsk launch commands discussed above. But in this Live disk, the Chkdsk utility has its own interface and is launched using a script. The shortcut to launch the utility is placed directly on the desktop.

In the drop-down list to check the disk, select the desired disk partition. Next, activate the checkboxes for restoring damaged sectors and forcibly disabling a partition (volume). Let's check the launches.


AdminPE's tools include a number of other utilities for working with hard drives, as well as the well-known programs Hard Disk Sentinel and Victoria.
Have a great day!
One day it may turn out that a PC or laptop refuses to start the Windows operating system or freezes during important and urgent work. Hard drive errors when running Windows are not the last reason for computer failure. However, any problem can be corrected if you know what its cause is.
The essence of the disk problem
Whether it is a traditional hard drive or a newfangled SSD drive, a critical error appears anywhere on it. Disk error - physically or software damaged sectors, system infection Windows viruses, failures in PC components (from parts of the drive itself to components motherboard computer). The user's task is to figure out what caused the errors on the disk.
How to fix hard drive problems detected by Windows
Hard drive problems are unspecified errors on it that are not signed with a numeric code (for example, error 11). First of all, the media from which it is proposed to copy valuable data is indicated.
Windows warns you that your data could be seriously damaged
Action plan:
- Urgent copying important files to another storage device: flash drives, disks, memory cards, placing some of these files on “cloud” Internet services.
- Checking the disk for bad sectors.
- Antivirus scanning.
- Checking the CMOS/BIOS settings on your computer.
- PC maintenance: checking the integrity of the cables, external inspection of PC components and cleaning them.
- If you find faults that you could not fix on your own, take your PC or laptop in for repair.
The last two points will not be considered - this is the task of specialists at computer service centers.
Backing up files in Windows 7
Do the following.
- Click “Start” and enter the word “backup” in the search bar of the Windows main menu. Launch the Backup and Restore application.
 Click on the first option offered - this is the backup wizard
Click on the first option offered - this is the backup wizard - Start setting up your archiving program. Click "Customize" backup».
 Get started setting up your backup
Get started setting up your backup - Select the disk or partition where backups will be created. External drives and flash drives or large-capacity memory cards (from ten gigabytes) are best suited.
 Select another, healthy and working disk
Select another, healthy and working disk - Click on "Give Windows a choice." However, if you have clearly decided what you need first, choose the independent option.
 If you give the system a choice, Windows will copy the contents of all user folders by default
If you give the system a choice, Windows will copy the contents of all user folders by default - Select system folders user files and/or the contents of copied disks - except for the disk on which the copy will be created.
 Select everything you want to copy except the destination drive
Select everything you want to copy except the destination drive - Windows will ask for confirmation and display the categories of files being sent to backup storage.
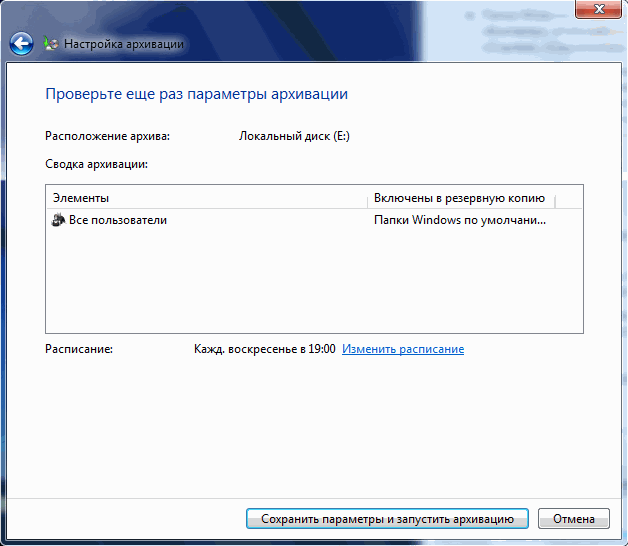 After this, the system will ask you to double-check the settings and start copying
After this, the system will ask you to double-check the settings and start copying
To recover files from backup copy do the following:

The process will start. After the copying is complete, check if everything has been restored.
 Click the link that appears to view a list of files and folders from the previous copy
Click the link that appears to view a list of files and folders from the previous copy Checking the disk using the Windows 7 command line
Disk scan identifies logically or physically problematic sectors of the hard drive or SSD drive, which is the main one in the computer. Do the following:

If you still don’t trust standard disk checking tools, use the Victoria program. The Victoria version for Windows is almost the same as the version for DOS - with one exception: after downloading, you can immediately run it to check a disk running a still working Windows system, without resorting to other disks, including removable ones.
Also get a new disk - in case the old one has outlived its usefulness.
Checking your PC for viruses
Boot viruses corrupt the boot record and the NTFS(5) file table, with which Windows 7 works. Because of this, valuable data that is not easy to recover with special utilities, as well as the system itself, is lost.
As an example, use the Dr. utility. Web CureIt, allowing you to quickly check HDD for the presence of malicious code.

The application takes up more than 100 MB - due to the extensive anti-virus database of all times. After two days of work, this database is considered outdated - viruses appear almost hourly.
If an error appears when starting Windows
The computer refuses to boot from the hard drive, reporting a read error system files Windows.
 To try to resolve the hard drive read error, press Ctrl+Alt+Del to restart
To try to resolve the hard drive read error, press Ctrl+Alt+Del to restart A professional way to resolve such an error is a third-party disk check utility with bootable media Windows or another operating system (if there is a version of this utility for it).
Checking the disk using built-in tools hides some details, although its use is not useless.
What makes no sense to do:
- restore the Windows system to an earlier date;
- run automatic recovery;
- start Windows safe mode.
Setting up the BIOS to boot your PC from a flash drive or external drive
Change the PC boot priority from different drives in the BIOS. Do the following (the Award BIOS version is taken as an example).
- When you turn on the computer, after the manufacturer's logo appears (or immediately below it), a prompt line to enter the BIOS will appear - press this key.
 Press the key indicated at the end of the list of devices scanned when turning on the PC
Press the key indicated at the end of the list of devices scanned when turning on the PC - After entering BIOS Setup, select “Integrated Peripherals”.
 To enter component management, select Integrated Peripherals
To enter component management, select Integrated Peripherals - Check if the USB port controller is active.
 USB Controller Enabled means that the USB controller is enabled
USB Controller Enabled means that the USB controller is enabled - If USB support is enabled, exit this submenu using the Esc key. If it is disabled, enable USB support using the Page Up\Down keys (the meanings of all keys for managing BIOS settings are revealed below), then exit by pressing Esc.
- From the main BIOS menu, select Advanced BIOS settings».
 Go to the advanced BIOS settings to control how your PC boots from different types carriers
Go to the advanced BIOS settings to control how your PC boots from different types carriers - Enter the hard drive priority menu and turn on the flash drive as the first boot drive.
 To configure the system, the boot order from media must be changed
To configure the system, the boot order from media must be changed - Use the “+” or “Page UP/Down” key to designate the flash drive as the first boot device.
 The first place in the boot list should be a flash drive.
The first place in the boot list should be a flash drive. - Exit this submenu by pressing Esc and set USB drives as the first device to be launched.
 Set the USB-HDD parameter in the First Boot Device section (First boot from a USB drive)
Set the USB-HDD parameter in the First Boot Device section (First boot from a USB drive) - Exit all submenus to the main BIOS menu and press F10 to save the settings.
 When a message appears asking the BIOS to save settings, press Y and Enter
When a message appears asking the BIOS to save settings, press Y and Enter - Give the command “Y” - “Enter”, the computer will restart.
Now, when you restart the PC, it will first poll the ports for the presence of a flash drive or removable hard drive (HDD/SSD) - and only then try to start Windows from the built-in disk.
Checking a hard drive from a flash drive running the Victoria program
For example, we took a ready-made flash drive with Victoria under DOS and a laptop with a faulty disk. Do the following.
- Insert the USB flash drive and restart the PC. Should come out boot menu with Victoria.
 In the window that appears, select Victoria
In the window that appears, select Victoria - Victoria app can offer different versions- select the version for laptops.
 In the Victoria for Notebook section, select the second option
In the Victoria for Notebook section, select the second option - If you want to familiarize yourself with Victoria's functionality, read the key help by pressing F1.
 First, find out how to launch different functions of the Victoria program by pressing F1
First, find out how to launch different functions of the Victoria program by pressing F1 - To exit the help, press the X key or any other key that is not in the list.
 To exit the help, press X and go to Check Disk
To exit the help, press X and go to Check Disk - From the main menu, press F2 to display disk information. If this does not happen, press the P key to select the IDE interface channel on which the disk sits. All modern PCs are equipped with SATA hard drives.
 In the window that appears, select Ext. PCI ATA/SATA and press Enter
In the window that appears, select Ext. PCI ATA/SATA and press Enter - After selecting the channel type, enter its number, for example, 1. If there are no other hard drives, the following numbers will be empty, there is no point in entering them.
 Busy channels in the program are immediately visible - enter the channel number of your disk and press Enter
Busy channels in the program are immediately visible - enter the channel number of your disk and press Enter - Wait until Victoria detects the disk on channel 1.
 A message indicating successful channel detection will appear at the bottom
A message indicating successful channel detection will appear at the bottom - If your disk turns out to be IDE-based, go back to the interface selection submenu and select one of the options Primary/Secondary Master/Slave (English: “Primary/Secondary Main/Auxiliary disk”) - check on the disk itself what position it is in switch. IDE is obsolete - modern SATA-based drives do not require switching. The Primary Master mode is taken as an example.
 Select the mode with the cursor keys and confirm the selection with the Enter key
Select the mode with the cursor keys and confirm the selection with the Enter key - The disk details will appear at the bottom. Press F2 to display information.
 The channel port number is attached to the disk information
The channel port number is attached to the disk information - Initialization (passport data) of the disk shows that its recognition by the Victoria application has been completed.
 After the disk is fully initialized, you can start checking it
After the disk is fully initialized, you can start checking it - Press F4 - the disk scanning menu will appear. Here LBA is a disk sector (512 bytes). We multiply the number of LBA sectors by 512, divide by 1024 3 - we get the size in gigabytes. The size of the disk area being scanned in Victoria for DOS should not exceed 1024 GB. If the size is more than 1 TB, calculate the beginning (Start LBA) and end (EndLBA) and scan the disk in several stages.
 Check that the disk size does not exceed 1 TB
Check that the disk size does not exceed 1 TB - Press the spacebar and enter an integer number in gigabytes or percentage - this will determine the location of the last sector in the scanned area. The scanning start point is also changeable - similarly calculate the size in gigabytes. When you're finished typing, press Enter.
 Enter the last gigabyte that will end the scanned disk area
Enter the last gigabyte that will end the scanned disk area - The size of the scanned disk area will be recalculated into the number of LBA sectors. Go to linear reading. Do not change this reading algorithm to another (random and “floating” reads will take longer and wear out the already old disk more).
 Select the program's linear disk scanning mode
Select the program's linear disk scanning mode - Go to the next item and select “BB (Bad Blocks) Advanced Remap”. Options are selected using the left/right cursor keys or the space bar.
 Select the BB Advanced Remap option - it will use sectors from the spare area
Select the BB Advanced Remap option - it will use sectors from the spare area - Don’t rush to set the “Erase 256 sect.” algorithm. (“Erasing 256 adjacent sectors”) - in place of one problematic sector, 128 KB of data on the disk will be erased. In this case, the size of the destroyed information will be multiplied by the number of “broken” sectors - depending on the proximity of each of these sectors to each other throughout the scanned area of the disk. Try other sector recovery options first! Press "Enter" to start scanning.
That's it, the process has begun, the Victoria application will notify you of completion with the sound of a beep on the computer. When bad sectors are found, “remapping” (reassignment of sectors) will be automatically performed.
 Replacing bad sectors using Victoria is one of the effective ways to temporarily fix a hard drive
Replacing bad sectors using Victoria is one of the effective ways to temporarily fix a hard drive The future operation of the disk can be predicted based on SMART monitoring data. Press F9. The status will be indicated at the top. If it is “Good”, there is still a reserve for replacing bad sectors. The status has changed - the disk will be replaced with a new one. If it is not possible to replace the disk, try to programmatically trim it, excluding the bad sectors from the cropped area (often they are close to each other, many of them in a row), but this is for those who like difficulties.
 The Good status indicates that the disk is in good condition.
The Good status indicates that the disk is in good condition. Other ways to check the disk
There are several options:
- using other applications recorded on a flash drive in a similar way (DOS bootloader);
- scandisk.exe utility launched through DOS using the appropriate commands;
- team Windows string XP running from LiveCD/DVD;
- connecting the problematic drive to another computer via a free cable.
Video: checking and trimming “broken” space
Error 11 when writing or unpacking data
The “11th error” has nothing to do with damaged sectors on the disk. This is 90% a software problem. It occurs when installing unverified programs that have installation sources that were compiled by the developers with some omissions. The message is generated by the system library unarc.dll, which is responsible for unpacking content for any installed program and is one of the components of the Windows Installer service.
 Error code 11 can be replaced by any code from 1 to 10
Error code 11 can be replaced by any code from 1 to 10 Some users, not understanding the problem with the source code of the installed program, update or replace this file (it “lies” in the C:\Windows\System32 directory) with any version of it from the Internet. As a result, Windows may report that some files have been replaced with unknown versions, and require you to insert an installation DVD or flash drive to restore them.
The solutions to the problem are as follows:
- try not to allow Russian names of files and folders in installed applications. For example, instead of the \Truckers-2 folder, when installing the game “Truckers-2”, the \Rig&Roll folder is created. If, after all, the directory name is written in Cyrillic, it means the game is from a dubious source, download the licensed one (hacking the version does not matter, as long as it has a file structure like the licensed source);
- There is not enough disk space (in any of its partitions) for the program to be installed. Clean the disk from unnecessary programs, documents and other content;
- error unpacking archives downloaded from the Internet. Install several archivers (for example, WinRar, WinZip, 7zip and several others);
- disable your antivirus and Windows firewall- sometimes they become an obstacle, especially if any application or game requires crack (activator with key selection).
Other hard drive errors
They may be:
- 3f1 (the error is inherent in HP laptops);
- 300 (boot record not detected);
- 3f0 (no boot disk);
- 301 (SMART disk health diagnostic error), etc.
Video: checking partition C: and flash drives for errors in Windows 7/8/10
Restoring the functionality of a PC or laptop in the event of disk failures is not a problem if you act wisely and consistently. May you be lucky!